
Publishing a classified balance sheet also makes it easy for regulators to point out an issue in the initial stages rather than in the final stages when irrevocable damage has already been done. It shows the value of the company’s ownership after all debts are paid. It’s important for users of a classified balance sheet to be aware of these limitations and to use the balance sheet as just one tool in their overall analysis of a company’s financial health.
Impact on Operational Strategy – The Strategic Role of Asset and Liability Classification
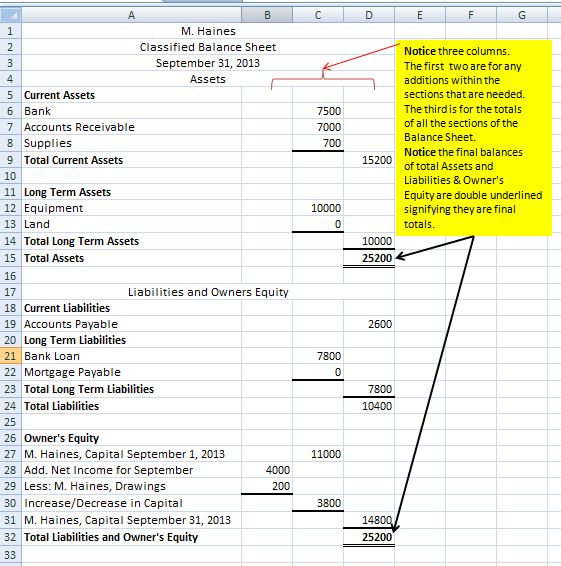
When the data has been set into the right classifications, you’ll add every section separately. At the point when that is finished, you’ll need to add each one of the subtotals to show up at your asset total, which is $98200. A similar rule holds for the Liabilities section, where you’ll list every single current liability, just as those that are long term, like other loans and mortgages. The Current Assets list incorporates all assets that have an expiry date of less than one year. The Fixed Assets category records things like land or a structure, while assets that don’t fit into ordinary classifications are placed in the Other Assets classification. Taking a look at the balance sheet of RMS Pvt Ltd you will notice that the assets have been categorized into three different groups as Total Fixed Assets, Total Current Assets, and Total Other Assets.
Variations in Classified Balance Sheets in Different Countries – The Global Perspective
Currents assets are further listed under this category on basis of liquidity such that most liquid item is at top of list and rest are listed from most liquid to least liquid. Category of current assets include cash and equivalent, account receivable, inventories, prepaid expenses, and other short term nature assets. In our classified balance sheet, we make sure to list total assets, total liabilities, and total shareholders’ equity clearly.
A Guide to Balance Sheets with Template
The most widely recognized current liabilities are accrued expenses and Accounts payable. Creating a functional and easily managed classified balance sheet begins with your software. The more customizable and configurable your technology, the more you can aggregate the data into classifications for management. Additionally, make sure the chart of accounts is flexible, letting you group and manage accounts to fit your individual needs.
The right column is for listing liabilities, which you total and add to the owners’ equity. When the sum of liabilities and owners’ equity is totalled, the amount should be equal to the total amount of assets in the left column. When completing your taxes or providing financial information to regulatory authorities. In some cases, businesses are required to submit their balance sheet and other financial statements for tax purposes. These standards ensure consistency, transparency, and comparability across balance sheets.
- An important characteristic is that they can be easily liquidated to generate cash, which helps a business meet any short-term liquidity crunches.
- For example, you can take totals of current assets and current liabilities in the classified balance sheet to calculate the current ratio.
- Along these lines, this part is constantly reflected in the current section.
They are often capital-intensive and are critical for long-term strategic planning. However, a classified balance sheet is detail-oriented, polished, and audited. Most of the time, the classified balance sheet has accompanying notes to report details of all items. Current are the possessions of a company that can be liquidated within 12 months. Some of the current assets have very high liquidity and can be used as a substitute for cash. This article will walk through a classified balance sheet format, benefits of the classified balance sheet, formating, and general classifications included.
All in all, it segregates every one of the balance sheet accounts into simpler subgroups to make a more valuable and significant report. The board can decide on what kinds of subcategories to use, yet the most recognized happen classified balance sheet template to be long-term and current. Determining your business’s ability to meet current financial obligations or defining your working capital. To do this, you will need to know your company’s current ratio and days cash on hand.
An unclassified balance sheet does not have sub-totals, clearly defined categories, and accompanying notes. Long-term investments are the assets of the company that cannot be liquidated within 12 months. These investments can be long-term debt securities, equity shares, or real estate properties.
It provides detailed insights into a company’s financial health, helping stakeholders make informed decisions regarding liquidity, solvency, and long-term financial strategy. The nuanced interpretation of a classified balance sheet extends beyond a mere understanding of a company’s financial position at a given time. How assets and liabilities are categorized can have long-term strategic implications, heavily influenced by the industry within which a company operates. With a classified balance sheet, investors, creditors, and other stakeholders can easily assess a company’s liquidity by looking at the current assets and liabilities. Similarly, the long-term or non-current assets and liabilities give stakeholders a clearer picture of the company’s long-term financial stability. These classifications mainly include current and non-current sections for both assets and liabilities.
It’s like a snapshot of the company’s financial health, sorted in a way that makes it easy to read and understand. The classified balance sheet provides a clearer snapshot of the company’s financial structure compared to a standard balance sheet, allowing for detailed analysis. Similarly, liabilities are categorized into current and non-current or long-term liabilities. Current liabilities include obligations expected to be settled within a year, such as accounts payable and accrued expenses. Long-term liabilities, like long-term debt or lease obligations, are due beyond a year.
“Current liabilities” are debts the company needs to pay back soon, like a bill from a supplier. “Long-term liabilities” are debts that don’t need to be paid back for a long time, like a big loan to buy a building. For example, if a company has a lot of long-term assets like buildings and patents, it might mean the company is set up to make money for a long time.